Highlights
Black cohosh, a herb with many purported uses and benefits, has been widely used for treating women’s health conditions, especially menopause symptoms. Few studies found that the use of isopropanolic extract of Black cohosh with or without St John’s wort may reduce menopause symptoms in breast cancer patients who were treated with Endocrine therapies such as Tamoxifen. A study also suggested an increase in recurrence-free survival in breast cancer women who used an isopropanolic extract of Black cohosh. However, in spite of these possible benefits, more well designed clinical studies which evaluate its safety are required before recommending black cohosh use in cancer patients undergoing treatments as there are high possibilities of undesired herb-drug interactions and side-effects. Hence, avoid using these herbal supplements and medications while on breast cancer treatment unless suggested by your health care practitioners.
What is Black Cohosh?
Black cohosh (Actaea racemosa/Cimicifuga racemosa) is a perennial herb that is native to North America. The root and the rhizome of this herb have been traditionally used for medicinal purposes by the native Indian population.

Following are some of the key active constituents of Black Cohosh:
- Phytosterin
- Isoferulic acid
- Tannins
- Salicylic acid
- Caffeic acid
- Ferulic acid
- Sugars
- Long-chain fatty acids
- Cinnamic acid
- Fukinolic acid
- Cimicifugic acid
- Dihydroxyphenyl lactic acid
- Acetein
Purported Uses/Benefits of Black Cohosh
Black Cohosh has many potential benefits/purported uses owing to its anti-inflammatory, antihistamine and antioxidant properties. Most of the purported uses/benefits of black cohosh are related to women’s health, and ample evidence on its benefits are available only for a few conditions, especially menopause symptoms.
Other health conditions for which black cohort has been used in spite of insufficient evidence include:
- Heart disease
- Osteoarthritis
- Infertility
- Migraine
- Osteoporosis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Anxiety
Side-Effects of Black Cohosh
It is usually safe when taken in the right amounts by adults. However, it may cause some side-effects such as :
- Headache
- Rash
- Weight gain
- Stomach upset
- Vaginal bleeding/spotting
- Cramping
- A feeling of heaviness
Apart from the side-effects mentioned above, one should also be wary of the following, if taking black cohosh:
- It might cause liver damage and autoimmune hepatitis in some patients, although no conclusive evidence is available to confirm this.
- It may not be safe for pregnant women.
- It may worsen certain hormone-sensitive conditions due to their estrogenic effect.
- Along with alfalfa, it may lead to kidney transplant rejection.
- It might increase the risk of blood clots in people with a protein S deficiency.
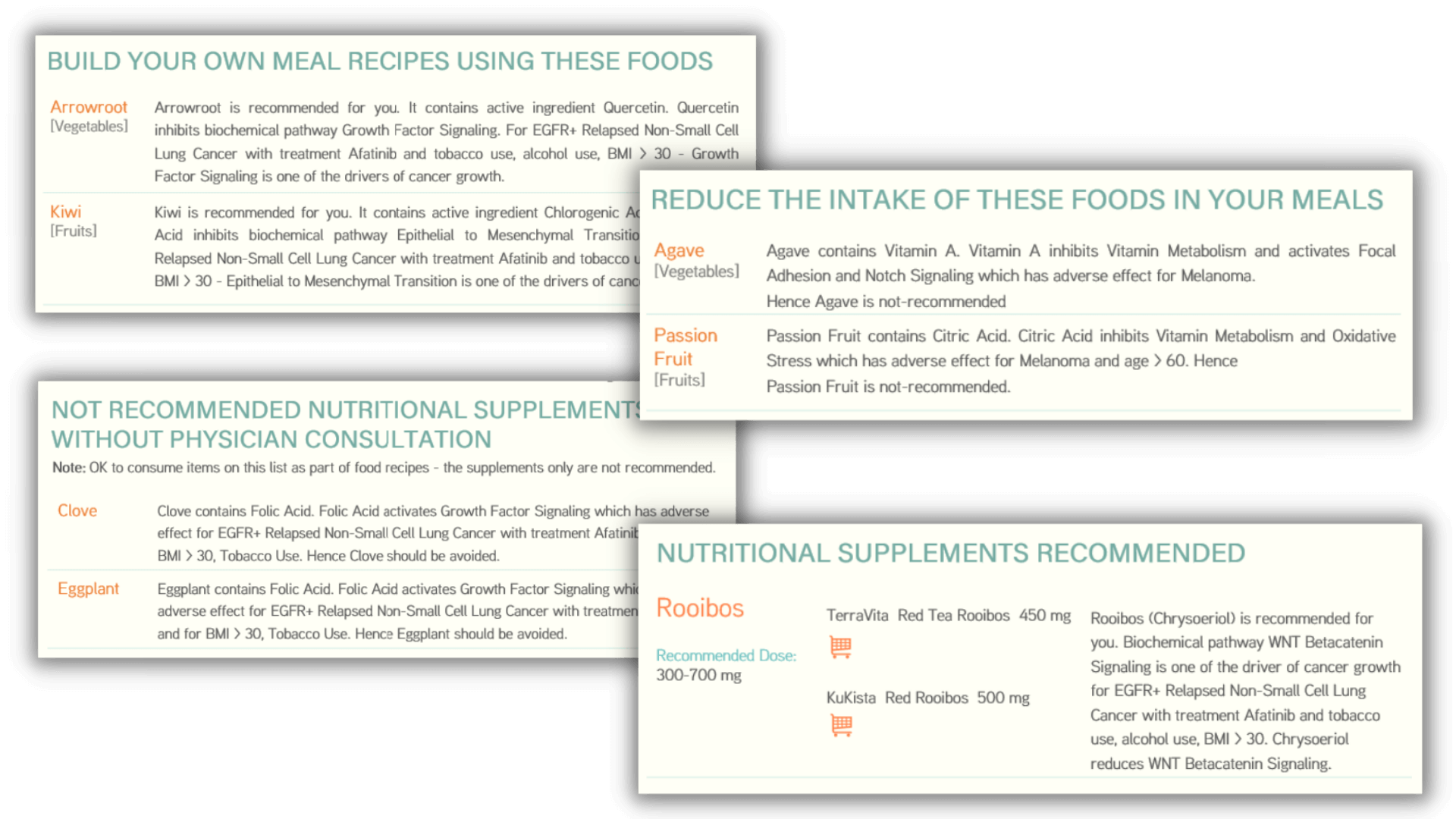
Foods to Eat After Cancer Diagnosis!
No two cancers are the same. Go beyond the common nutrition guidelines for everyone and make personalized decisions about food and supplements with confidence.
Clinical Use/Possible Benefits of Black Cohosh in Breast Cancer Patients
Endocrine therapy or Hormonal therapy such as Tamoxifen is one of the most common treatments used for breast cancer, especially in the estrogen receptor positive breast cancers. However, these treatments may result in severe ‘climacteric’ or menopause symptoms in breast cancer survivors including adverse reactions like hot flushes, sleep problems, depressive symptoms, irritability, and mood swings. Several approaches have been tried out for handling such symptoms in breast cancer patients including the use of herbal medications.
In this blog, we will explore different studies carried out to evaluate the effect of using black cohosh for handling menopause symptoms in breast cancer patients. In many of these studies, a specific isopropanolic extract of black cohosh is used to study the impact. Remifemin, a herbal medicine used to relieve menopause complaints, is one of the most studied black cohosh supplements used in different clinical trials as well as open-label studies for monitoring its effects in physicians’ practices.
Use of Isopropanolic extract of Black Cohosh alone or in Combination with St John’s wort in Breast Cancer Patients with Menopausal Symptoms Receiving Endocrine Therapy
Through a systematic literature search done by the researchers from the Capital Medical University in Beijing, China, University Hospitals of Tuebingen, Blankenstein Hospital and Schaper & Brümmer GmbH & Co. KG in Germany, they evaluated whether menopausal symptoms in Breast cancer patients who received Endocrine therapy (Tamoxifen) can be treated with an isopropanolic extract of Black Cohosh alone or in combination with St John’s wort. The intent of the study was to offer orientation for health care providers by giving an overview of the experimental and clinical data on the efficacy and safety of using Isopropanolic extract of Black Cohosh with or without St John’s wort, its use in breast cancer patients, and putative interactions with the endocrine treatment. (X Ruan et al, Climacteric., 2019)
For this, data was obtained through search in MEDLINE, EMBASE, EMBASE Alert, BIOSIS, and PubMed databases for clinical studies with Isopropanolic extract of Black Cohosh alone or in combination with St John’s wort (Remifemin/Remifemin plus) and the specific St John’s wort component in the herbal combinations.
Key Findings of the study:
- Isopropanolic extract of Black Cohosh alone or in combination with St John’s wort reduced menopausal symptoms in most breast cancer survivors receiving endocrine therapy.
- There were no estrogen-like effects at the breast or on hormones.
- If receiving tamoxifen after breast cancer, those who used isopropanolic extract of Black Cohosh alone or in combination with St John’s wort had a significantly increased recurrence-free survival rates compared to non-users.
The researchers didn’t find any adverse events or serious side-effects due to herb-drug interactions in these patients treated with Black cohosh. Hence, they concluded that the isopropanolic extract of Black Cohosh alone or in combination with St John’s wort may offer a safe non-hormonal therapeutic option for breast cancer survivors receiving endocrine therapy such as Tamoxifen.
Use of Black cohosh in Tamoxifen-treated Breast Cancer Patients with Menopausal Symptoms
A previous study done by the researchers from University Hospital in Zurich, Switzerland also carried out a prospective observational study in 50 breast cancer patients who were treated with tamoxifen. These patients previously had surgery, 87% had undergone radiation therapy and around 50% had received chemotherapy. All 50 patients were treated with an isopropanolic extract of black cohosh for 6 months. (Matthias Rostock et al, Gynecol Endocrinol., 2011)
The study found an overall reduction in menopause symptoms with black cohosh treatment. While there were improvements in hot flashes, sweating, sleep problems, and anxiety, symptoms like urogenital and musculoskeletal complaints did not change with black cohosh treatment. The study found adverse events in 22 patients but highlighted that none of these were linked with the black cohosh medication. 90% of the patients under the study also reported good tolerability of the extract.
The researchers concluded Black cohosh extract to be a reasonable treatment approach in tamoxifen treated breast cancer patients with predominantly psychovegetative symptoms such as hot flashes, sweating, sleep problems, and anxiety improved.
Impact of Isopropanolic Using Black Cohosh Extract on Recurrence-free Survival in Breast Cancer Patients
In another previous study, the researchers from Schaper & Brümmer GmbH & Co. KG, Salzgitter in Germany, evaluated the effect of an isopropanolic Black cohosh extract on recurrence-free survival after breast cancer, including estrogen-dependent tumors. A total of 18,861 breast patients were included in the study of which 1102 patients received an isopropanolic Black cohosh extract therapy.
After a mean observation time of 3.6 years, it was found that isopropanolic Black cohosh extract therapy was not associated with an increase in the risk of recurrence, and even led to a prolonged disease-free survival. While 14% of the breast cancer patients who did not receive Black cohosh developed a recurrence after 2 years following initial diagnosis, the patients who received isopropanolic Black cohosh extract therapy reached this proportion only after 6.5 years. (H H Henneicke-von Zepelin et al, Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther., 2007)
However, more well designed clinical studies are needed to confirm these findings as well as evaluate the safety and efficacy of using Isopropanolic black cohosh extract, especially while undergoing treatment to avoid any undesired herb-drug interactions and side-effects.
Herb-Drug Interactions
Before using any herbal medications along with cancer treatments, it is important to look for any possible herb-drug interactions that can harm the cancer treatment and worsen the cancer.
Tamoxifen is metabolized into its active metabolite called endoxifen mainly via cytochrome P450 enzymes CYP2D6 and CYP3A4.
It is usually considered that Black cohosh is unlikely to affect the pharmacokinetics of conventional drugs which are metabolized by CYP1A2, CYP2D6, CYP2E1 and CYP3A4.(Sompon Wanwimolruk et al, EXCLI J., 2014) However, an experimental study mentioned that at 50 µg/ml, a 75% ethanolic extract of black cohosh inhibited the formation of 4-hydroxy-tamoxifen by 66.3%, N-desmethyl tamoxifen by 74.6% and α-hydroxy tamoxifen by 80.3%. (Jinghu Li et al, Xenobiotica., 2011) Hence, whether there are clinically relevant interactions of Black cohosh with Tamoxifen which can impact the therapy’s efficacy is not very clear.
St John’s wort is a herbal supplement known to have a number of clinically significant interactions. St John’s wort may not influence CYP2D6 significantly, but it is well known to induce CYP3A4.(X Ruan et al, Climacteric., 2019) Theoretically, a CYP3A4 induction could increase the metabolism of the hormonal drug tamoxifen into its active metabolite endoxifen, and may even lead to an enhancement of tamoxifen efficacy. However, one needs to be careful that increased concentrations of endoxifen are not way too high that can in turn lead to other serious drug toxicities. Hence, if using black cohosh with St John’s wort in patients undergoing treatment with Tamoxifen, it becomes really important to optimize the dosage of the drug (possibly a lowered dosage) and the herbal medication.
Conclusion
Black cohosh has been widely used for treating menopausal symptoms. Few studies found that the use of isopropanolic extract of Black cohosh with or without St John’s wort may reduce menopausal symptoms in breast cancer patients treated with Tamoxifen therapy. A study also suggested that, an increase in the risk of breast cancer recurrence for women who used an isopropanolic extract of Black cohosh when compared to those women who didn’t use it, is unlikely. However, this evidence may not be sufficient enough to recommend using black cohosh for improving recurrence-free survival in breast cancer patients. Additionally, though there are studies showing reduction in menopausal symptoms in breast cancer patients treated with Tamoxifen therapy post using isopropanolic extract of Black cohosh with or without St John’s wort, it is important to deep dive into the possible herb-drug interactions that can happen to ensure safety while using such herbal medications alongside a cancer treatment.
While St John’s wort present in the herbal combination may increase the endoxifen levels (the active metabolite of tamoxifen) which theoretically may improve the drug efficacy, one should be wary of the possibility that the concentrations of endoxifen may increase way too high which can in turn lead to other serious drug toxicities. Hence, breast cancer patients undergoing treatment should not use these herbal supplements containing black cohosh and St Johns wort without discussing with their health care practitioners to stay away from side-effects.
What food you eat and which supplements you take is a decision you make. Your decision should include consideration of the cancer gene mutations, which cancer, ongoing treatments and supplements, any allergies, lifestyle information, weight, height and habits.
The nutrition planning for cancer from addon is not based on internet searches. It automates the decision making for you based on molecular science implemented by our scientists and software engineers. Irrespective of whether you care to understand the underlying biochemical molecular pathways or not - for nutrition planning for cancer that understanding is needed.
Get started NOW with your nutrition planning by answering questions on the name of cancer, genetic mutations, ongoing treatments and supplements, any allergies, habits, lifestyle, age group and gender.
Personalized Nutrition for Cancer!
Cancer changes with time. Customize and modify your nutrition based on cancer indication, treatments, lifestyle, food preferences, allergies and other factors.
Cancer patients often have to deal with different chemotherapy side effects which affect their quality of life and look out for alternative therapies for cancer. Taking the right nutrition and supplements based on scientific considerations (avoiding guesswork and random selection) is the best natural remedy for cancer and treatment related side-effects.
