Highlights
Bamboo is widely recognized for its health benefits and is frequently used by cancer patients and those at genetic risk. Yet, the safety and effectiveness of Bamboo for cancer patients depend on many factors like the cancer indication, chemotherapy, other treatments, and the tumor’s genetics. Knowing that some foods and supplements, such as grapefruit and spinach, might interact poorly with cancer medications and cause adverse reactions is crucial.
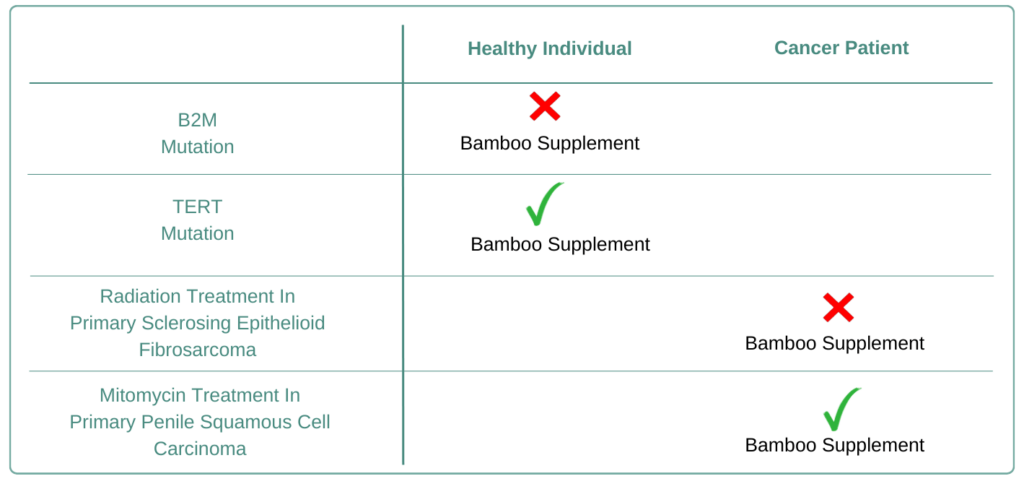
Diet is critical for cancer treatment as it can affect treatment outcomes. Cancer patients must carefully select and incorporate suitable foods and supplements into their diets. For example, Bamboo could benefit those with Primary Penile Squamous Cell Carcinoma undergoing Mitomycin, but it might not be good for patients receiving Radiation for Primary Sclerosing Epithelioid Fibrosarcoma. Furthermore, while Bamboo could help individuals with a genetic risk factor “TERT”, it may not be suggested for those with a different genetic risk “B2M”. Personalizing diet plans based on health, treatment, and genetics is essential.
Understanding that making a decision on the suitability of Bamboo for a cancer patient needs to be individualized is crucial. Critical factors like the type of cancer, treatment methods, genetic makeup, genetic risks, age, body weight, and lifestyle are vital in deciding if Bamboo is the appropriate choice. Genetics and genomics, in particular, is a significant consideration. Since these factors can evolve, it’s essential to regularly review and adapt dietary choices to match changes in health status and treatment.
In conclusion, a holistic approach to dietary choices is vital, focusing on the overall effects of all active components in foods/supplements like Bamboo instead of assessing each active ingredient separately or ignoring it completely. This broad perspective fosters a more rational and scientific approach to diet planning for cancer.
Brief Overview
Use of plant-based foods and supplements, such as vitamins, herbs, minerals, probiotics, and various specialized supplements, are rising among cancer patients. These supplements are designed to deliver high concentrations of specific active ingredients, many of which are also in different foods. The concentration and diversity of active ingredients differ between whole foods and supplements. Foods typically offer a range of active ingredients but at lower concentrations, while supplements provide higher concentrations of specific ingredients.
Considering the varied scientific and biological functions of each active ingredient at the molecular level, it’s crucial to account for the combined effects of these components when deciding on foods and supplements to eat or not.

The critical question arises: Should you incorporate Bamboo into your diet as a food item or a supplement? Is it advisable to consume Bamboo if you have a genetic predisposition to cancer associated with the TERT gene? What if instead your genetic risk stems from the B2M gene? Is it beneficial to include Bamboo in your diet if you’re diagnosed with Primary Sclerosing Epithelioid Fibrosarcoma, or if your diagnosis is Primary Penile Squamous Cell Carcinoma? Moreover, how should your consumption of Bamboo be adjusted if you’re undergoing Mitomycin treatment or if your treatment plan shifts from Mitomycin to Radiation? It’s essential to recognize that simplistic assertions like ‘Bamboo is natural, so it’s always beneficial’ or ‘Bamboo boosts immunity’ are insufficient for informed food/supplement choices.
Additionally, it’s essential to reassess the appropriateness of including Bamboo in your diet if there are changes in your treatment regimen. In summary, when making decisions about incorporating foods or supplements like Bamboo into your diet for its benefits, you should consider the overall biochemical effects of all ingredients, considering factors such as the type of cancer, the specific treatments you’re undergoing, genetic predispositions, and lifestyle choices.
Cancer
Cancer remains a significant challenge in the medical field, often causing widespread anxiety. However, recent advancements have improved treatment outcomes, notably through personalized treatment approaches, non-invasive monitoring methods using blood and saliva samples, and the development of immunotherapy. Early detection and timely intervention have been crucial in positively influencing overall treatment outcomes.
Genetic testing offers significant promise in evaluating cancer risk and susceptibility early on. However, for many individuals with familial and genetic predispositions to cancer, options for therapeutic intervention, even with regular monitoring, are often limited or none. Once diagnosed with a specific type of cancer, such as Primary Penile Squamous Cell Carcinoma or Primary Sclerosing Epithelioid Fibrosarcoma, treatment strategies need to be customized based on the individual’s tumor genetics, the stage of the disease, as well as factors like age and gender.”
Post-treatment, ongoing monitoring is essential to detect any signs of cancer relapse and to inform subsequent decisions. Many cancer patients and those at risk often seek advice on incorporating certain foods and supplements into their diets, which plays a crucial role in their overall decision-making process regarding health management.
The critical question is whether to factor in genetic risks and specific cancer diagnoses when deciding on dietary choices, such as Bamboo. Does a genetic risk for cancer stemming from a mutation in the TERT have the same biochemical pathway implications as a mutation in the B2M? From a nutritional standpoint, does the risk associated with Primary Penile Squamous Cell Carcinoma equate to Primary Sclerosing Epithelioid Fibrosarcoma? Furthermore, does the dietary consideration remain the same for those undergoing Radiation as for those receiving Mitomycin? These considerations are crucial in making informed food choices for individuals with different genetic risks and cancer treatments.
Bamboo – A Nutritional Supplement
The supplement Bamboo encompasses a range of active ingredients, including Vitamin C, Tricin, Palmitic Acid, Oleic Acid and Linolenic Acid, each present at varying concentrations. These ingredients influence molecular pathways, specifically Cell Cycle Checkpoints, TGFB Signaling, Chemokine Signaling and Oncogenic Cancer Epigenetics, which regulate critical aspects of cancer at the cellular level, such as tumor growth, spread, and cell death. Given this biological influence, selecting the appropriate supplements like Bamboo, alone or in combination, becomes a critical decision in the context of cancer nutrition. When considering using Bamboo for cancer, it’s essential to consider these various factors and mechanisms. This is because, similar to cancer treatments, the use of Bamboo is not a universal decision suitable for all cancers but needs to be personalized.
Choosing Bamboo Supplements
Addressing the question ‘When should I avoid Bamboo in the context of Cancer’ is challenging because the answer is highly individualized – it simply ‘Depends!’. Similar to how any cancer treatment may not be effective for every patient, the relevance and safety or benefits of Bamboo varies depending on personal circumstances. Factors such as the specific type of cancer, genetic predispositions, current treatments, other supplements being taken, lifestyle habits, BMI, and any allergies all play a role in determining whether Bamboo is appropriate or should be avoided, underlining the importance of personalized consideration in such decisions.
Foods to Eat After Cancer Diagnosis!
No two cancers are the same. Go beyond the common nutrition guidelines for everyone and make personalized decisions about food and supplements with confidence.
1. Will Bamboo Supplements benefit Primary Sclerosing Epithelioid Fibrosarcoma Patients undergoing Radiation treatment?
Primary Sclerosing Epithelioid Fibrosarcoma is characterized by particular genetic mutations, namely PBRM1, ATRX and PIK3C2G, which lead to alterations in biochemical pathways, specifically TGFB Signaling and Inositol Phosphate Signaling. The effectiveness of a cancer treatment, such as Radiation, is contingent on its mechanism of action on these specific pathways. The ideal strategy involves aligning the treatment’s action with the pathways driving the cancer, thereby ensuring a personalized and effective approach. In such scenarios, avoiding foods or nutritional supplements that might counteract the treatment’s effects or diminish this alignment is crucial. For instance, the Bamboo supplement, which affects the TGFB Signaling, may not be the right choice in the case of Primary Sclerosing Epithelioid Fibrosarcoma when undergoing Radiation. This is because it may either exacerbate the disease’s progression or interfere with the treatment’s efficacy. When choosing a nutrition plan, it’s important to consider factors such as cancer type, ongoing treatments, age, gender, BMI, lifestyle, and any known genetic mutations.
2. Will Bamboo Supplements benefit Primary Penile Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients undergoing Mitomycin Treatment?
Primary Penile Squamous Cell Carcinoma is identified by specific genetic mutations, such as ABRAXAS1, PIK3CB and NUP93, which result in changes in biochemical pathways, particularly Cell Cycle Checkpoints, Hematopoiesis and Inositol Phosphate Signaling. The efficacy of a cancer treatment, like Mitomycin, is determined by its interaction with these pathways. The aim is to ensure that the treatment aligns well with the pathways that drive the cancer, enabling a personalized treatment approach. In this context, foods or supplements that are compatible with the treatment or enhance this alignment should be considered. For example, the Bamboo supplement is a rational option for those with Primary Penile Squamous Cell Carcinoma undergoing Mitomycin. This is because Bamboo influences pathways such as Cell Cycle Checkpoints, which can either inhibit the factors driving Primary Penile Squamous Cell Carcinoma or benefit the effectiveness of the Mitomycin.
3. Are Bamboo Supplements Safe for Healthy Individuals with B2M Mutation Associated Genetic Risk?
Various companies provide gene panels for assessing the genetic risk of different types of cancers. These panels include genes linked to breast, ovarian, uterine, prostate, and gastrointestinal cancers. Testing these genes can confirm a diagnosis and inform treatment and management strategies. Identifying a variant that causes disease can further assist in the testing and diagnosing of relatives who may be at risk. The B2M gene is commonly included in these panels for cancer risk assessment.
A mutation in the B2M gene affects biochemical pathways or processes, such as Chemokine Signaling and Antigen Presentation, which are directly or indirectly involved in driving cancer at the molecular level. When a genetic panel identifies a mutation in the B2M associated with an increased risk of Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma, scientific rationale suggests avoiding use of supplement Bamboo. This is because supplement Bamboo influences pathways like Chemokine Signaling, which can lead to adverse effects in the context of the B2M mutation and related cancer conditions.
4. Are Bamboo Supplements Safe for Healthy Individuals with TERT Mutation Associated Genetic Risk?
TERT plays a crucial role in cancer risk assessment. Mutations in TERT can disrupt critical biochemical pathways, including Oncogenic Cancer Epigenetics and DNA Repair, which influence cancer development. If your genetic panel reveals mutations in TERT associated with Hematological Cancer, consider incorporating Bamboo supplements in your nutrition plan. These supplements can positively influence pathways like Oncogenic Cancer Epigenetics, benefit by providing relevant support for individuals with TERT mutations and related health concerns.
In Conclusion
The two most important things to remember are that cancer treatments and nutrition are never the same for everyone. Nutrition, including food and supplements like Bamboo for its benefits, is an effective tool that can be controlled by you while facing cancer.
“What should I eat?” is the most commonly asked question by cancer patients and those at-risk of cancer. The correct response is that it depends on factors such as cancer type, genetics of tumor, current treatments, allergies, lifestyle, and BMI.
Get your nutrition personalization for cancer from addon by clicking the link below and answering questions about your cancer type, treatment, lifestyle, allergies, age, and gender.
Personalized Nutrition for Cancer!
Cancer changes with time. Customize and modify your nutrition based on cancer indication, treatments, lifestyle, food preferences, allergies and other factors.
References
- Genetically defined subsets of human pancreatic cancer show unique in vitro chemosensitivity.
- The synergy of Vitamin C with decitabine activates TET2 in leukemic cells and significantly improves overall survival in elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia.
- cBioPortal for Cancer Genomics
- Cancer therapy shapes the fitness landscape of clonal hematopoiesis.
- α-Linolenic Acid Inhibits Receptor Activator of NF-κB Ligand Induced (RANKL-Induced) Osteoclastogenesis and Prevents Inflammatory Bone Loss via Downregulation of Nuclear Factor-KappaB-Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthases (NF-κB-iNOS) Signaling Pathways.
- Alpha linolenic acid and oleic acid additively down-regulate malignant potential and positively cross-regulate AMPK/S6 axis in OE19 and OE33 esophageal cancer cells.
- Mutational landscape of metastatic cancer revealed from prospective clinical sequencing of 10,000 patients.
- Separation and purification of tricin from an antioxidant product derived from bamboo leaves.
