Introduction
Foods for Non-hodgkin Lymphoma should be personalized for each individual and also must adapt when cancer treatment or tumor genetic change. The personalization and adaptation must consider all the active ingredients or bioactives contained in different foods with respect to cancer tissue biology, genetics, treatments, lifestyle conditions and diet preferences. Hence while nutrition is one of the very important decisions for a cancer patient and individual at risk of cancer to make – how to choose foods to eat is not an easy task.
Non-hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) is the seventh most common cancer in men and the sixth most common cancer in women. The disease accounts for 4% of all cancers in the United States. The survival rate has been improving since 1997, due to the treatment advances. 5-year survival for patients with non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma is almost 86.5% when diagnosed at an early stage, but when it is spread and disseminated, the 5-year survival rate is 64%. (Seer.cancer.gov)
Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma is a group of blood cancers that begin in the cells of the lymphatic system, which is a part of the immune system that helps the body fight infection and disease. There are many different types of non-Hodgkin lymphoma that form from different types of immune cells such as the B-cells, T-cells, and Natural killer (NK) cells. Most common types of aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphomas develop in the B-cells, and they include:
• Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL)
• Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL)
• Acute lymphoblastic lymphoma (ALL)
• Burkitt lymphoma
The aggressive T-cell non-Hodgkin cell lymphomas include:
• Peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL)
• Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL)
• Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL)
• Hepatosplenic gamma/delta T-cell lymphoma
The slow growing indolent types of non-Hodgkin lymphomas include
• Follicular lymphoma
• Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
• Marginal zone lymphoma (MZL)
• Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia
• Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
Common symptoms of NHL include swollen lymph nodes, belly pain or swelling, chest pain, cough, trouble breathing, persistent fatigue, unexplained fever, heavy night sweats, unexplained weight loss and others. Treatment options include watchful waiting and active surveillance for slow growing indolent lymphomas, while the treatment options for the aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphomas include systemic chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, radiation therapy and stem cell transplantation. Treatment supported by a healthy lifestyle and the right personalized nutrition (foods and natural supplements) can help improve patient well-being.
For Non-hodgkin Lymphoma does it matter what vegetables, fruits, nuts, seeds one eats?
A very common nutrition question asked by cancer patients and individuals at-genetic risk of cancer is – for cancers like Non-hodgkin Lymphoma does it matter what foods I eat and which I do not? Or if I follow a plant-based diet is that enough for cancer like Non-hodgkin Lymphoma?
For example does it matter if vegetable Cabbage is consumed more compared to Calabash? Does it make any difference if fruit Muscadine Grape is preferred over Highbush Blueberry? Also if similar choices are made for nuts/seeds like Common Walnut over Brazil Nut and for pulses like Moth Bean over Lima Bean. And if what I eat matters – then how does one identify foods which are recommended for Non-hodgkin Lymphoma and is it the same answer for everyone with the same diagnosis or genetic risk?
Yes! Foods you eat matters for Non-hodgkin Lymphoma!
Food recommendations may not be the same for everyone and can be different even for the same diagnosis and genetic risk.

All foods (vegetables, fruits, nuts, seeds, pulses, oils etc.) and nutritional supplements are made up of more than one active molecular ingredient or bio-actives in different proportions and quantities. Each active ingredient has a unique mechanism of action – which can be activation or inhibition of different biochemical pathways. Simply stated foods and supplements which are recommended are those which do not cause an increase of molecular drivers of cancer but reduce them. Else those foods should not be recommended. Foods contain multiple active ingredients – hence when evaluating foods and supplements you need to consider the impact of all active ingredients cumulatively rather than individually.
For example Muscadine Grape contains active ingredients Curcumin, Lupeol, Isoliquiritigenin, Genistein, Myricetin. And Highbush Blueberry contains active ingredients Quercetin, Gallic Acid, Curcumin, Lupeol, Isoliquiritigenin and possibly others.
A common mistake made when deciding and choosing foods to eat for Non-hodgkin Lymphoma – is to evaluate only selected active ingredients contained in foods and ignore the rest. Because different active ingredients contained in foods may have opposing effects on cancer drivers – you cannot cherry pick active ingredients in foods and supplements for making a nutrition decision for Non-hodgkin Lymphoma.
YES – FOOD CHOICES MATTER FOR CANCER. NUTRITION DECISIONS MUST CONSIDER ALL ACTIVE INGREDIENTS OF FOODS.
Skills Needed for Nutrition Personalization for Non-hodgkin Lymphoma?
Personalized nutrition for cancers like Non-hodgkin Lymphoma consists of recommended foods / supplements; not recommended foods / supplements with example recipes which prioritize use of recommended foods. An example of personalized nutrition can be seen at this link.
Deciding which foods are recommended or not is extremely complicated, requiring expertise in Non-hodgkin Lymphoma biology, food science, genetics, biochemistry along with good understanding of how cancer treatments work and associated vulnerabilities by which the treatments could stop being effective.
MINIMUM KNOWLEDGE EXPERTISE NEEDED FOR NUTRITION PERSONALIZATION FOR CANCER ARE: CANCER BIOLOGY, FOOD SCIENCE, CANCER TREATMENTS AND GENETICS.
Foods to Eat After Cancer Diagnosis!
No two cancers are the same. Go beyond the common nutrition guidelines for everyone and make personalized decisions about food and supplements with confidence.
Characteristics of cancers like Non-hodgkin Lymphoma
All cancers like Non-hodgkin Lymphoma can be characterized by a unique set of biochemical pathways – the signature pathways of Non-hodgkin Lymphoma. Biochemical pathways like Chemokine Signaling, Oncogenic Cancer Epigenetics, Cytoskeletal Dynamics, Cell Junctions are part of the signature definition of Non-hodgkin Lymphoma. Each individual’s cancer genetics can be different and hence their specific cancer signature could be unique.
The treatments which are effective for Non-hodgkin Lymphoma need to be cognizant of the associated signature biochemical pathways for each cancer patient and individual at genetic risk. Therefore different treatments with different mechanisms of actions are effective for different patients. Similarly and for the same reasons foods and supplements need to be personalized for each individual. Hence some foods and supplements are recommended for Non-hodgkin Lymphoma when taking cancer treatment Acalabrutinib, and some foods and supplements are not recommended.
Sources like cBioPortal and many others provide population representative patient anonymized data from clinical trials for all cancer indications. This data consists of clinical trial study details like sample size / number of patients, age groups, gender, ethnicity, treatments, tumor site and any genetic mutations.
TET2, RHOA, EP300, COL3A1 and IDH2 are the top ranked reported genes for Non-hodgkin Lymphoma. TET2 is reported in 50.0 % of the representative patients across all clinical trials. And RHOA is reported in 37.5 %. The combined population patient data cover ages from 4 to 57. 73.9 % of the patient data are identified as men. The Non-hodgkin Lymphoma biology along with reported genetics together define the population represented signature biochemical pathways for this cancer. If the individual cancer tumor genetics or genes contributing to the risk are also known then that should also be used for nutrition personalization.
NUTRITION CHOICES SHOULD MATCH WITH EACH INDIVIDUAL’S CANCER SIGNATURE.
Food and Supplements for Non-hodgkin Lymphoma
For Cancer Patients
Cancer patients on treatment or on palliative care need to make decisions on food and supplements – for the needed dietary calories, for managing any treatment side effects and also for improved cancer management. All plant-based foods are not equal and choosing and prioritizing foods which are personalized and customized to ongoing cancer treatment is important and complicated. Here are some examples providing guidelines for making nutrition decisions.
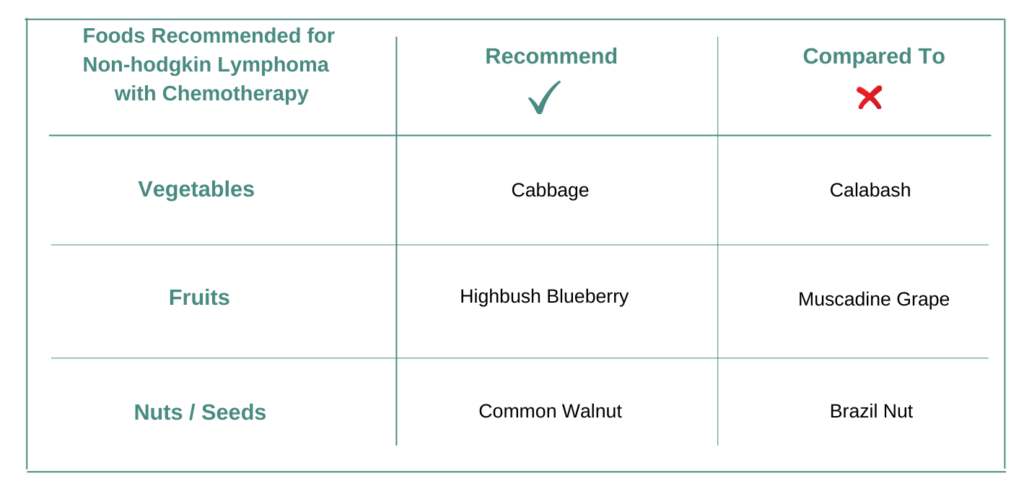
Choose Vegetable CABBAGE or CALABASH?
Vegetable Cabbage contains many active ingredients or bioactives such as Quercetin, Benzyl Isothiocyanate, Curcumin, Lupeol, Sulforaphane. These active ingredients manipulate various biochemical pathways like Apoptosis, NFKB Signaling and Oncogenic Cancer Epigenetics and others. Cabbage is recommended for Non-hodgkin Lymphoma when ongoing cancer treatment is Acalabrutinib. This is because Cabbage modifies those biochemical pathways which have been scientifically reported to sensitize the effect of Acalabrutinib.
Some of the active ingredients or bioactives in vegetable Calabash are Curcumin, Lupeol, Isoliquiritigenin, Genistein, Myricetin. These active ingredients manipulate various biochemical pathways like Calcium Signaling and Oncogenic Cancer Epigenetics and others. Calabash is not recommended for Non-hodgkin Lymphoma when ongoing cancer treatment is Acalabrutinib because it modifies those biochemical pathways which make the cancer treatment resistant or less responsive.
VEGETABLE CABBAGE IS RECOMMENDED OVER CALABASH FOR Non-hodgkin Lymphoma AND TREATMENT Acalabrutinib.
Choose Fruit HIGHBUSH BLUEBERRY or MUSCADINE GRAPE?
Fruit Highbush Blueberry contains many active ingredients or bioactives such as Quercetin, Gallic Acid, Curcumin, Lupeol, Isoliquiritigenin. These active ingredients manipulate various biochemical pathways like Apoptosis, Oncogenic Cancer Epigenetics and Netrin Signaling and others. Highbush Blueberry is recommended for Non-hodgkin Lymphoma when ongoing cancer treatment is Acalabrutinib. This is because Highbush Blueberry modifies those biochemical pathways which have been scientifically reported to sensitize the effect of Acalabrutinib.
Some of the active ingredients or bioactives in fruit Muscadine Grape are Curcumin, Lupeol, Isoliquiritigenin, Genistein, Myricetin. These active ingredients manipulate various biochemical pathways like NFKB Signaling and Oncogenic Cancer Epigenetics and others. Muscadine Grape is not recommended for Non-hodgkin Lymphoma when ongoing cancer treatment is Acalabrutinib because it modifies those biochemical pathways which make the cancer treatment resistant or less responsive.
FRUIT HIGHBUSH BLUEBERRY IS RECOMMENDED OVER MUSCADINE GRAPE FOR Non-hodgkin Lymphoma AND TREATMENT Acalabrutinib.
Choose Nut COMMON WALNUT or BRAZIL NUT?
Common Walnut contains many active ingredients or bioactives such as Quercetin, Gallic Acid, Curcumin, Lupeol, Isoliquiritigenin. These active ingredients manipulate various biochemical pathways like Apoptosis, Netrin Signaling, Inositol Phosphate Signaling and C-type Lectin Receptor Signaling and others. Common Walnut is recommended for Non-hodgkin Lymphoma when ongoing cancer treatment is Acalabrutinib. This is because Common Walnut modifies those biochemical pathways which have been scientifically reported to sensitize the effect of Acalabrutinib.
Some of the active ingredients or bioactives in Brazil Nut are Curcumin, Lupeol, Isoliquiritigenin, Genistein, Phloretin. These active ingredients manipulate various biochemical pathways like NFKB Signaling and Chemokine Signaling and others. Brazil Nut is not recommended for Non-hodgkin Lymphoma when ongoing cancer treatment is Acalabrutinib because it modifies those biochemical pathways which make the cancer treatment resistant or less responsive.
COMMON WALNUT IS RECOMMENDED OVER BRAZIL NUT FOR Non-hodgkin Lymphoma AND TREATMENT Acalabrutinib.
For Individuals with Genetic Risk of Cancer
The question asked by individuals who have genetic risk of Non-hodgkin Lymphoma or familial history is “What Should I Eat Differently from Before?” and how they should choose foods and supplements to manage risks of the disease. Since for cancer risk there is nothing actionable in terms of treatment – decisions of foods and supplements become important and one of the very few actionable things which can be done. All plant-based foods are not equal and based on identified genetics and pathway signature – the choices of food and supplements should be personalized.
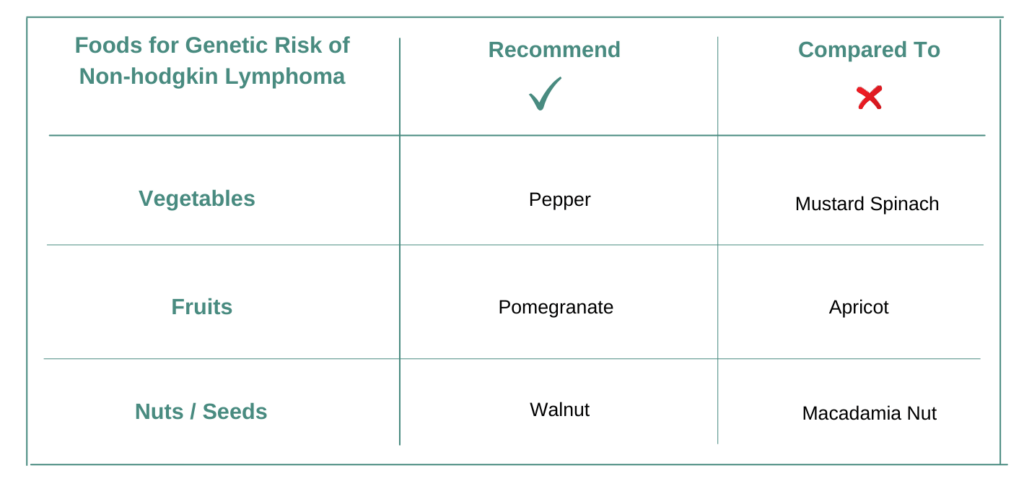
Choose Vegetable PEPPER or MUSTARD SPINACH?
Vegetable Pepper contains many active ingredients or bioactives such as Curcumin, Quercetin, Salicylic Acid, Isoliquiritigenin, Delphinidin. These active ingredients manipulate various biochemical pathways like TGFB Signaling, Hypoxia, WNT Beta Catenin Signaling and Growth Factor Signaling and others. Pepper is recommended for risk of Non-hodgkin Lymphoma when associated genetic risk is COL3A1. This is because Pepper increases those biochemical pathways which counteract the signature drivers of it.
Some of the active ingredients or bioactives in vegetable Mustard Spinach are Curcumin, Salicylic Acid, Isoliquiritigenin, Delphinidin, Phloretin. These active ingredients manipulate various biochemical pathways like WNT Beta Catenin Signaling and Oncogenic Cancer Epigenetics and others. Mustard Spinach is not recommended when risk of Non-hodgkin Lymphoma when associated genetic risk is COL3A1 because it increases the signature pathways of it.
VEGETABLE PEPPER IS RECOMMENDED OVER MUSTARD SPINACH FOR COL3A1 GENETIC RISK OF CANCER.
Choose Fruit POMEGRANATE or APRICOT?
Fruit Pomegranate contains many active ingredients or bioactives such as Curcumin, Quercetin, Salicylic Acid, Isoliquiritigenin, Ellagic Acid. These active ingredients manipulate various biochemical pathways like TGFB Signaling, WNT Beta Catenin Signaling, Focal Adhesion and Cytoskeletal Dynamics and others. Pomegranate is recommended for risk of Non-hodgkin Lymphoma when associated genetic risk is COL3A1. This is because Pomegranate increases those biochemical pathways which counteract the signature drivers of it.
Some of the active ingredients or bioactives in fruit Apricot are Curcumin, Quercetin, Salicylic Acid, Isoliquiritigenin, Delphinidin. These active ingredients manipulate various biochemical pathways like TGFB Signaling and WNT Beta Catenin Signaling and others. Apricot is not recommended when risk of Non-hodgkin Lymphoma when associated genetic risk is COL3A1 because it increases the signature pathways of it.
FRUIT POMEGRANATE IS RECOMMENDED OVER APRICOT FOR COL3A1 GENETIC RISK OF CANCER.
Choose Nut WALNUT or MACADAMIA NUT?
Walnut contains many active ingredients or bioactives such as Curcumin, Salicylic Acid, Isoliquiritigenin, Ellagic Acid, Delphinidin. These active ingredients manipulate various biochemical pathways like TGFB Signaling, Hypoxia, WNT Beta Catenin Signaling and Focal Adhesion and others. Walnut is recommended for risk of Non-hodgkin Lymphoma when associated genetic risk is COL3A1. This is because Walnut increases those biochemical pathways which counteract the signature drivers of it.
Some of the active ingredients or bioactives in Macadamia Nut are Curcumin, Salicylic Acid, Isoliquiritigenin, Delphinidin, Phloretin. These active ingredients manipulate various biochemical pathways like Growth Factor Signaling and Oncogenic Cancer Epigenetics and others. Macadamia Nut is not recommended when risk of Non-hodgkin Lymphoma when associated genetic risk is COL3A1 because it increases the signature pathways of it.
WALNUT IS RECOMMENDED OVER MACADAMIA NUT FOR COL3A1 GENETIC RISK OF CANCER.
In Conclusion
Foods and Supplements chosen are important decisions for cancers like Non-hodgkin Lymphoma. Non-hodgkin Lymphoma patients and individuals with genetic-risk always have this question: “What foods and nutritional supplements are recommended for me and which are not?” There is a common belief which is a misconception that all plant-based foods could be beneficial or not but would not be harmful. Certain foods and supplements can interfere with cancer treatments or promote molecular pathway drivers of cancer.
There are different types of cancer indications like Non-hodgkin Lymphoma, each with different tumor genetics with further genomic variations across each individual. Further every cancer treatment and chemotherapy has a unique mechanism of action. Each food like Cabbage contains various bioactives in different quantities, which have an impact on different and distinct sets of biochemical pathways. The definition of personalized nutrition is individualized food recommendations for the cancer indication, treatments, genetics, lifestyle and other factors. Nutrition personalization decisions for cancer require knowledge of cancer biology, food science and an understanding of different chemotherapy treatments. Finally when there are treatment changes or new genomics is identified – the nutrition personalization needs re-evaluation.
The addon nutrition personalization solution makes the decision making easy and removes all the guesswork in answering the question, “What foods should I choose or not choose for Non-hodgkin Lymphoma?”. The addon multi-disciplinary team includes cancer physicians, clinical scientists, software engineers and data scientists.
Personalized Nutrition for Cancer!
Cancer changes with time. Customize and modify your nutrition based on cancer indication, treatments, lifestyle, food preferences, allergies and other factors.
References
- Pediatric Dkfz 2017
- Mutational landscape of metastatic cancer revealed from prospective clinical sequencing of 10,000 patients.
- Paederia foetida induces anticancer activity by modulating chromatin modification enzymes and altering pro-inflammatory cytokine gene expression in human prostate cancer cells.
- Gallic acid inhibits gastric cancer cells metastasis and invasive growth via increased expression of RhoB, downregulation of AKT/small GTPase signals and inhibition of NF-κB activity.
- Estrogen receptor modulators genistein, daidzein and ERB-041 inhibit cell migration, invasion, proliferation and sphere formation via modulation of FAK and PI3K/AKT signaling in ovarian cancer.
- Betulinic Acid Suppresses Breast Cancer Metastasis by Targeting GRP78-Mediated Glycolysis and ER Stress Apoptotic Pathway.
- Melatonin and vitamin D3 synergistically down-regulate Akt and MDM2 leading to TGFβ-1-dependent growth inhibition of breast cancer cells.
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15662-non-hodgkin-lymphoma
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559328
- https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/nhl.html
