Highlights
Following a Mediterranean diet characterized by high intake of vegetables, legumes, fruits and nuts, cereals, fish, and a high ratio of unsaturated to saturated lipids, and higher intake of Vitamin E, folate and indole-3-carbinol may reduce the risk of human papillomaviruses (HPV) infections and cervical cancer and enhance the regression of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (the precancerous condition in which abnormal cells grow on the surface of the cervix). However, avoid high supplementation of copper and beta-carotene as well as obesity causing foods as these may increase the risk of cervical cancer. Taking the right diet with the right foods included, may help reduce the risk of the cancer and improve the treatment outcomes as well as reduce aggravation of symptoms in cervical cancer.
Cervical Cancer Incidence, Causes and Risk Factors
Cervical cancer is the cancer that develops in a woman’s cervix, the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. According to the World Health Organization, Cervical cancer is the fourth most common cancer in women. In 2018, globally, around 570 000 women were diagnosed with cervical cancer and 311000 deaths were reported due to cervical cancer.

Cervical cancer occurs when the healthy cells in the cervix develop changes or mutations in their DNA.
About 99% of cervical cancer cases are linked to a sexually transmitted infection, the high-risk human papillomaviruses (HPV) infection. Although HPV infections usually resolve faster, persistent infection may lead to cervical cancer in women.
Other Factors which causes Cervical Cancer include :
- Smoking
- Having more than 5 children especially at a very early age
- Weakened immune system
- Other sexually transmitted infections like gonorrhea, syphilis and HIV/AIDS increases the risk of human papillomaviruses (HPV)
- Mother taking hormonal drug diethylstilbestrol (DES) when pregnant, thereby increasing the child’s risk of developing cervical cancer later.
- Consuming oral contraceptive pills for more than 5 years
- Having many sexual partners
Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
In the early stages of cervical cancer, there may be no signs or symptoms.
As the disease progresses, some of the following signs and symptoms of cervical cancer may be experienced:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding during or after intercourse
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding between periods
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding after menopause
- Watery, bloody heavy vaginal discharge with a foul odor
- Pelvic pain
- Pain during intercourse
If you experience one or more of these symptoms, please consult your doctor, even though abnormal bleeding does not necessarily indicate cervical cancer.
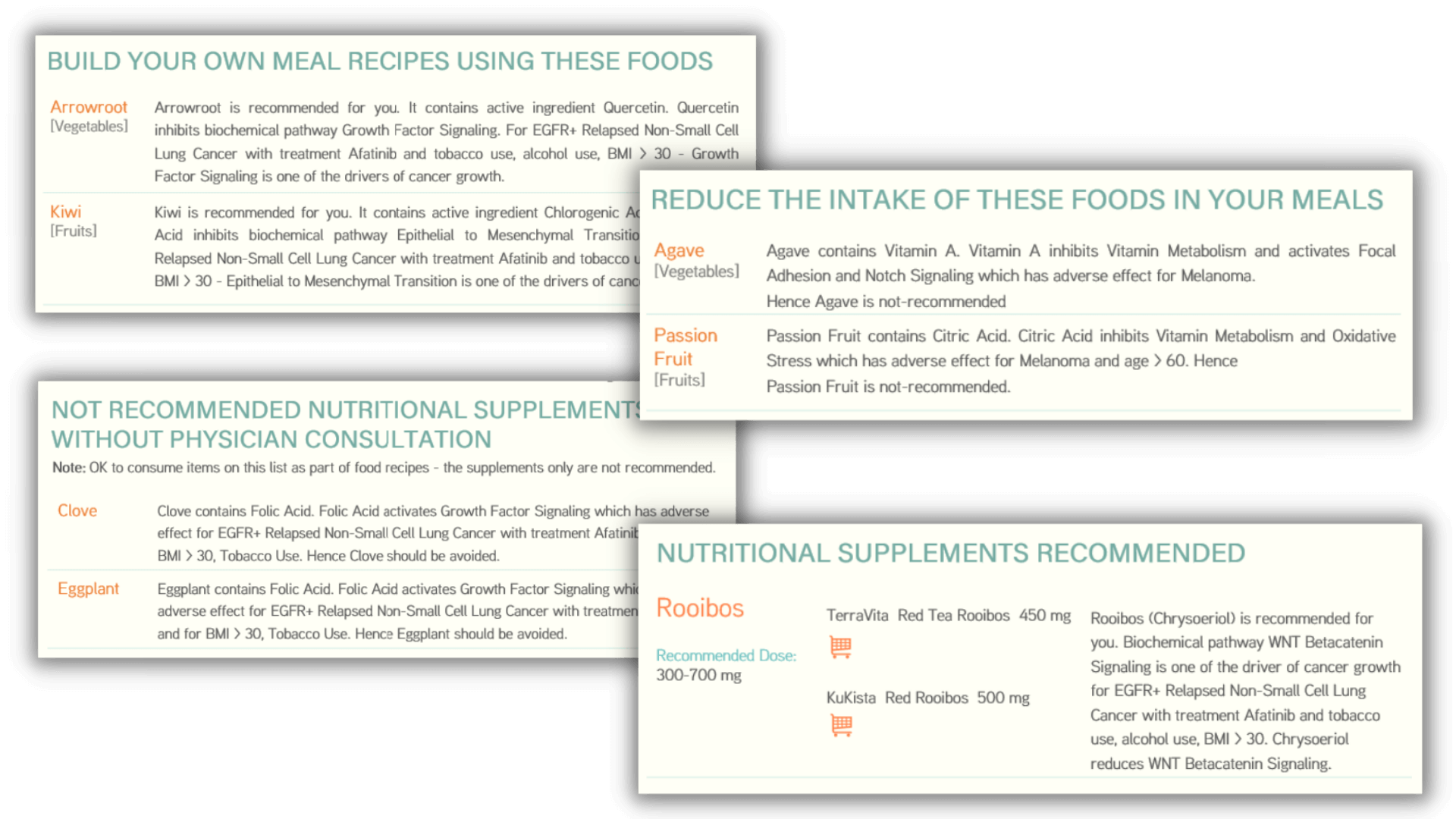
Foods to Eat After Cancer Diagnosis!
No two cancers are the same. Go beyond the common nutrition guidelines for everyone and make personalized decisions about food and supplements with confidence.
Treatments of Cervical Cancer
Finding out the stage of the cancer is important to decide on the most effective treatment for the cervical cancer patient. The stage of the cancer implies the extent of cancer spread/metastasis and tells us whether it is localized or has spread to nearby structures or distant parts/organs of the body.
There are various treatments available for Cervical cancer and is usually curable if it is diagnosed at an early stage. Depending on the type and stage of the cancer, and other factors such as age and general health conditions of the patient, the treatment may vary.
For early stages of cervical cancer, the treatment includes surgery to remove the cervix and some parts or all of the womb, or radiotherapy, or a combination of both surgery and radiotherapy. Radiation treatment may also help reduce the risk of cervical cancer recurrence.
For advanced cervical cancers, the treatment usually used is radiotherapy with or without chemotherapy, and in some cases, surgery too.
Avoid foods and supplements which can lead to adverse interactions with the cancer treatment if diagnosed with cervical cancer.
Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia is a precancerous condition in which abnormal cell growths are formed on the surface lining of the cervix. Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia is often treated with surgery to destroy the abnormal tissue. Rather than leading to the stage of treating cervical cancer post the cancer diagnosis, it is always better to get it detected at the precancerous stage and intervene earlier to prevent the development of this invasive disease.
Role of Diet in Cervical Cancer
Although smoking and HPV infections are considered as the major risk factors/causes for cervical cancer, diet may also play an important role in increasing or reducing the risk of this cancer. In this blog, we will have a look at some of the studies carried out by researchers across the world, which evaluated the association between the intake of different types of foods/diet and the risk of cervical cancer or regression of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia.
Copper Supplementation may Increase the Risk
A meta-analysis done by the researchers from the Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University in China based on data from 14 publications obtained through literature search in PubMed, WanFang, and China National Knowledge Internet (CNKI) databases till November 30, 2017, involving 747 patients with cervical cancer and 1014 controls, found higher serum copper levels in patients with cervical cancer than in control healthy subjects, suggesting that high Copper supplementation may increase the risk of cervical cancer. (Min Zhang et al, Biosci Rep., 2018)
Beta-Carotene Supplementation May Not Enhance the Regression of Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia
A previous study done by the researchers from the University of California evaluated the effect of daily beta-carotene supplementation in patients with grade 2 and 3 cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, which is a precancerous condition in which abnormal cells grow on the surface of the cervix. As part of the study, the researchers analyzed data from a total of 103 patients, who either received 30 mg beta-carotene or placebo (substance without therapeutic value). The researchers found that beta-carotene supplementation did not enhance the regression (reduction in size or extent) of high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, especially in those patients who were Human papillomavirus-positive. (K A Keefe et al, Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev., 2001)
Obesity may Increase the Risk
Researchers from Hamadan University of Medical Sciences and Islamic Azad University in Iran did a meta-analysis of 9 studies, obtained through literature search in PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, ScienceDirect, LILACS, and SciELO databases up to February 2015, involving 1,28,233 participants. The study found that obesity may be weakly associated with an increased risk of cervical cancer. (Jalal Poorolajal and Ensiyeh Jenabi, Eur J Cancer Prev., 2016)
Another retrospective cohort study of 944,227 women aged between 30 to 64 years who underwent cytology and human papillomavirus DNA testing at Kaiser Permanente Northern California between January 2003 and December 2015 found that overweight and obese women had an increased risk of cervical cancer, possibly because of under-diagnosis of cervical precancer. (Megan A Clarke et al, J Clin Oncol., 2018)
Hence, avoid obesity causing foods to reduce the risk of cervical cancer.
Higher Vitamin E Intake and Vitamin E Serum Levels may Reduce the Risk of Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia
A meta-analysis done by the researchers from the the Second Affiliated Hospital and Yuying Children’s Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University in China based on 15 case-control studies, obtained through literature search in PubMed, Embase and Cochrane databases through December 2016, involving 3741 patients with cervical neoplasia (the precancerous condition in which abnormal cells grow on the surface of the cervix) and 6328 controls, found that higher vitamin E intake and higher blood vitamin E levels were associated with a reduced risk of cervical neoplasia. (Xiaoli Hu et al, PLoS One., 2017)
Folate Supplementation May Help in the Regression of Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia
Researchers from Kashan University of Medical Sciences, Arak University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, and Tehran University of Medical Sciences in Iran, conducted a clinical study on 58 women, aged 18 to 55 years, who were diagnosed with grade 1 cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (the precancerous condition in which abnormal cells grow on the surface of the cervix) to determine the effects of long-term folate supplementation on regression and metabolic status of these patients. Out of 58 patients, 29 patients received 5 mg/d folate supplements for 6 months. The researchers found that folate supplementation among women with grade 1 cervical intraepithelial neoplasia resulted in its regression (reduction in size or extent) as well as improved certain metabolic factors. (Zatollah Asemi et al, Nutrition., 2016)
Indole-3-carbinol Supplementation May Help in the Regression of Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia
Researchers from the Louisiana State University Medical Center-Shreveport in the United States evaluated data from 30 patients with Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia who either received placebo or 200, or 400 mg/day of oral indole-3-carbinol. They found that out of the 10 patients in the group that received placebo, none had a complete regression of Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia, whereas 4 out of 8 patients in the group that received 200 mg/day of oral indole-3-carbinol had complete regression of Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia and 4 out of 9 patients in the group that received 400 mg/day of oral indole-3-carbinol had complete regression of Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia. (M C Bell et al, Gynecol Oncol., 2000)
Meditaerranean Diet may Reduce the Risk of HPV Infection and Cervical Cancer
Researchers from the University of Catania in Italy carried out a study on 539 women, including 127 with grade 2 cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and found that women who followed a Mediterranean Diet (characterized by a high intake of vegetables, legumes, fruits and nuts, cereals, fish, and a high ratio of unsaturated to saturated lipids) had a decreased risk of human papillomaviruses (HPV) infection, whereas those women who followed a Western Diet (characterized by a high intake of chips, snacks, dipping sauces, plant oils, processed and red meats, with low intake of olive oil) had an increased risk of HPV infection and cervical cancer. (Martina Barchitta et al, Nutrients., 2018)
Conclusion
These studies indicate that following a Mediterranean diet characterized by high intake of vegetables, legumes, fruits and nuts, cereals, fish, and a high ratio of unsaturated to saturated lipids, and higher intake of Vitamin E, folate and indole-3-carbinol found in cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli, brussels sprouts, cabbage, cauliflower, kale and bok choy may reduce the risk of cervical cancer or cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. However, avoid high intake of copper and beta-carotene supplements as well as obesity causing foods as these may result in increased risk of cervical cancer. Taking human papillomaviruses (HPV) vaccine, undergoing regular cervical screening, avoiding smoking, doing regular exercises, maintaining a healthy weight and following a diet with the right foods and supplements included may help to stay away from Cervical cancer and reduce aggravation of the symptoms.
What food you eat and which supplements you take is a decision you make. Your decision should include consideration of the cancer gene mutations, which cancer, ongoing treatments and supplements, any allergies, lifestyle information, weight, height and habits.
The nutrition planning for cancer from addon is not based on internet searches. It automates the decision making for you based on molecular science implemented by our scientists and software engineers. Irrespective of whether you care to understand the underlying biochemical molecular pathways or not - for nutrition planning for cancer that understanding is needed.
Get started NOW with your nutrition planning by answering questions on the name of cancer, genetic mutations, ongoing treatments and supplements, any allergies, habits, lifestyle, age group and gender.
Personalized Nutrition for Cancer!
Cancer changes with time. Customize and modify your nutrition based on cancer indication, treatments, lifestyle, food preferences, allergies and other factors.
Cancer patients often have to deal with different chemotherapy side effects which affect their quality of life and look out for alternative therapies for cancer. Taking the right nutrition and supplements based on scientific considerations (avoiding guesswork and random selection) is the best natural remedy for cancer and treatment related side-effects.
