Highlights
Consuming spices such as turmeric, fruits such as banana and avocado, drinking coffee, following a Mediterranean diet with vegetables including certain cruciferous vegetables, fruits, whole grains such as sorghum, button mushrooms and fish, and taking folate rich foods might help in reducing the risk of developing mouth/oral cancer and oropharyngeal cancer. To stay away from oral cancer, avoid smoking or chewing tobacco, and limit/avoid alcohol consumption – the two main factors which cause this cancer. When it comes to oropharyngeal cancer care and prevention, consuming certain foods such as cauliflower, cocoa, peppermint, mustard and currant may not be beneficial, and dietary supplements of cabbage, nutmeg, poppy, clove and fava bean should be avoided. Hence, following a personalized nutrition plan becomes a fundamental part of any cancer therapy including oral cavity/mouth and oropharyngeal cancer and may help in improving the treatment outcomes and alleviating the symptoms.
Oral Cavity/Mouth and Oropharyngeal Cancer
Oral cavity or Mouth cancer is one of several types of cancers categorized as Head and Neck Cancers. Mouth Cancer refers to the cancer that develops in any part of the mouth, such as:
- Lips
- Gums
- Surface of the Tongue
- Inside of the cheeks
- Roof of the mouth- palate
- Floor of the mouth (under the tongue)
Oropharyngeal cancer is a type of head and neck cancer which develops in the oropharynx, the part of the throat directly behind the mouth.
The treatments used for mouth and oropharyngeal cancer are mostly similar to those used for Head and Neck Cancers.

Cancer Incidence Rate
The World Health Organization estimated around 657,000 new cases of cancers of the oral cavity each year with more than 330,000 deaths. Oral cancer accounts for about 3% of all cancers diagnosed annually in the United States. Oropharyngeal cancer incidence is comparatively lower with only about 3 cases per 100,000 people per year.
Oral cavity cancers are highly common in the Asian countries. In countries such as Sri Lanka, India, Pakistan and Bangladesh, oral cancer is in fact the most common cancer. However, oropharyngeal cancers are more common in Caucasians than Asians. Both oral and oropharyngeal cancers are more common in men than in women and the risk increases with age.
The overall 5-year survival rate for patients diagnosed with oral or oropharyngeal cancer is 65%, suggesting that around 6 in 10 patients with mouth cancer may live for at least 5 years after their diagnosis. (Cancer Facts & Figures 2020, American Cancer Society)
Risk Factors
It is not very clear what exactly causes the mutations in the squamous cells (flat thin cells that line the lips and the inside of the mouth and throat) that lead to mouth cancer and oropharyngeal cancer.
Some of the common risk factors which causes oral cavity/mouth cancer and oropharyngeal cancer include:
- Drinking alcohol
- Deleterious oral habits such as tobacco chewing, betel-quid chewing, tobacco smoking, reverse smoking
- Infection with the Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
- Inherited genetic conditions such as Fanconi anemia and Dyskeratosis congenita
- Weakened immune system
Apart from these, excessive sun exposure to the lips might also cause mouth cancer.
Foods to Eat After Cancer Diagnosis!
No two cancers are the same. Go beyond the common nutrition guidelines for everyone and make personalized decisions about food and supplements with confidence.
Symptoms of Oral Cavity/Mouth and Oropharyngeal cancer
The symptoms of Oral Cavity/Mouth and Oropharyngeal Cancer include:
- Painful mouth ulcers which do not heal for several weeks
- Persistent lumps in the mouth or the neck that do not go away
- Loose teeth or sockets that do not heal after tooth extraction
- Persistent numbness on the lip or tongue
- White or red patches on the lining of the mouth, tongue, gums or tonsil
- Sore throat
- Difficulty in swallowing
- Changes in speech (lisp)
- Mouth pain
- Ear pain
Many a times, these symptoms may not be caused due to oral cavity/mouth and oropharyngeal cancer. However, if you experience any of the above symptoms related to oral cavity/mouth and oropharyngeal cancers, get it checked by your doctor or dentist.
Treatment Options for Mouth and Oropharyngeal Cancer
There are many types of treatments used for mouth and oropharyngeal cancers including surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy and a combination of these. Usually, post surgery, a course of radiation treatment may be provided to help prevent cancer recurrence.
However, the standard treatments for mouth/oropharyngeal cancer might also cause complications including difficulty in swallowing, speaking and so on. Hence, the treatments used should also aim to support preserving the vital functions of the mouth including breathing, speaking and eating.
To stay away from this life threatening disease, one should avoid smoking or chewing tobacco, and drinking alcohol which can cause mouth cancer and oropharyngeal cancer, and follow a healthy and balanced diet.
What is the Role of Diet/Foods in Oral/Mouth and Oropharyngeal Cancers?
Although smoking tobacco and drinking alcohol are considered as the major risk factors/causes for oral cavity/mouth cancer and oropharyngeal cancer, diet may also play an important role in increasing or reducing the risk of these cancers. In this blog, we will have a look at some of the studies carried out by researchers across the world, which evaluated the association between the intake of different types of foods/diet and the risk of oral cavity/mouth or oropharyngeal cancer.
Diet/Foods that may Reduce the Risk of Oral/Mouth or Oropharyngeal Cancer
Including Cruciferous Vegetables in the Diet may decrease the Risk of Oral Cancer
In a meta-analysis done by the researchers from various Universities in Italy, France and Switzerland, they evaluated the association between the intake of cruciferous vegetables and the risk of different types of cancers. For the analysis, a total of 1468 cancers of the oral cavity/pharynx and 11,492 controls were included. The study found that, as compared to those who did not consume or occasionally consumed cruciferous vegetables, consumption of cruciferous vegetables at least once a week significantly reduced the risk of cancer of the oral cavity or mouth/pharynx by 17%. (C Bosetti et al, Ann Oncol., 2012)
Findings from the study suggested that including cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli, kale, spinach, and brussels sprouts to the diet might help reduce the risk of oral cavity/mouth cancer. Cruciferous vegetables, in general, are considered as a healthy food for cancer patients diagnosed with various types of cancers including oral cavity/mouth and oropharyngeal cancer, and may even support their ongoing cancer treatments as well as alleviate the disease symptoms.
However, taking some of these vegetables such as cauliflower and mustard, and supplements of cabbage may not help when it comes to oropharyngeal cancers.
Including Vegetables and Fruits in the Diet may Decrease the Risk of Oral Cancer
In a meta-analysis done by the researchers from the University of Catanzaro Magna Graecia in Catanzaro, Italy, they evaluated the effect of fruit and vegetable intakes on the occurrence of oral/mouth cancer. The analysis was based on data from 16 studies, including 15 case-control studies and 1 cohort study, obtained through literature search for articles published up to September 2005. 2 separate meta-analyses were conducted for fruit and vegetable consumption. The study found that each portion of fruit consumed per day significantly reduced the risk of oral/mouth cancer by 49%. It was also found that vegetable consumption significantly reduced the overall risk of oral/mouth cancer by 50%. (Maria Pavia et al, Am J Clin Nutr. 2006)
Findings from the study suggest that including foods such as vegetables and fruits to the diet might help reduce the risk of oral cavity/mouth cancer.
Coffee Intake may Reduce the Risk of Oral and Oropharyngeal Cancer
- In 2013, the American Journal of Epidemiology published the analysis of data from the Cancer Prevention Study II, a prospective United States cohort/population-based study which was initiated in 1982 by the American Cancer Society, which involved 968,432 men and women who were cancer free at the time of enrollment. During 26 years of follow-up, a total of 868 deaths were reported for oral/mouth or pharyngeal cancer. The study found that drinking more than 4 cups of caffeinated coffee per day was associated with a 49% reduced risk of deaths due to oral/mouth or pharyngeal cancer as compared with no or occasional caffeinated coffee intake. The study also found that drinking more than two cups of decaffeinated coffee a day decreased the risk of oral/mouth or pharyngeal death by approximately 39%. However, the study didn’t find any association between tea consumption and oral/mouth cancer risk. (Janet S Hildebrand et al, Am J Epidemiol., 2013)
- Researchers from the University Institute of Health Sciences (IUCS-N) in Portugal also evaluated the association between coffee and oral/mouth and pharyngeal cancer. Data for this analysis was obtained from 13 case-control and 4 cohort/population-based studies through an electronic search of publications till August 2016 from PubMed, National Library of Medicines Medline, Embase, Science Direct and the Cochrane Central Register. The study found that coffee intake reduced the risk of oral cavity/mouth cancer by 18% and pharyngeal cancer by 28%. (J Miranda et al, Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal., 2017)
- Another study done by the researchers from the Central South University in Hunan, China also evaluated the effect of coffee consumption on the risk of oral/mouth cancer based on 11 case-control studies and 4 cohort/population-based studies, comprising 2,832,706 controls and 5021 cases of oral/mouth cancer, obtained through literature search in Pubmed and Embase till 2015. The study found that compared to those who did not drink or rarely drank coffee, people with high coffee consumption had a 37% reduced risk of oral cavity/mouth cancer. (Ya-Min Li et al, Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol., 2016)
Findings from these studies suggest that including coffee to the diet might help reduce the risk of oral cavity/mouth and oropharyngeal cancer.
Following a Mediterranenan Diet may Reduce the Risk of Oral and Oropharyngeal Cancer
A study done by the researchers from the Lausanne University Hospital in Switzerland and different universities in Milan, Italy evaluated the role of the Mediterranean diet on oral cavity/mouth and pharyngeal cancer. The analysis included data from a case-control study which was conducted between 1997 and 2009 in Italy and Switzerland, involving 768 oral cavity/mouth and pharyngeal cancer cases and 2078 hospital controls. The study found that following a Mediterranean diet rich in minimally processed fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, fish and olive oil significantly lowered the risk of developing oral/mouth and oropharyngeal cancer. (M Filomeno et al, Br J Cancer., 2014)
When it comes to oropharyngeal cancer, a diet including fruits such as banana and avocado; whole grain such as sorghum; fish; turmeric containing curcumin (Lei Zhen et al, Int J Clin Exp Pathol., 2014); and button mushrooms; may be beneficial.
Milk and Dairy Food Consumption may possibly Reduce the Risk of Oral Cavity/Mouth Cancer
A meta-analysis done by the researchers from the Zhejiang University in China evaluated the role of milk and dairy products consumption on oral/mouth cancer risk based on data from 12 publications, involving 4635 cases and 50777 participants, obtained through literature search in PubMed, Embase and Chinese Wanfang databases until 30 June 2019. The results from their analysis suggested that milk and dairy products consumption may be associated with decreased risk of oral or oropharyngeal cancer. (Jian Yuan et al, Biosci Rep., 2019)
Findings from this study suggest that including milk and milk products/dairy foods to the diet might help reduce the risk of oral cavity/mouth or oropharyngeal cancer; although a previous study suggested that milk may be associated with a non-significant increase in the risk of oropharyngeal cancer (F Bravi et al, Br J Cancer., 2013).
Folate Intake may Reduce the risk of Oral Cavity/Mouth and Oropharyngeal Cancer Risk
Analysis of data from 10 case-control studies which participated in the INHANCE (International Head and Neck Cancer Epidemiology) Consortium, including 5,127 oral/mouth/pharyngeal cancer cases and 13,249 controls, by the researchers from the IRCCS-Istituto di Ricerche Farmacologiche Mario Negri in Milan, Italy found that folate intake reduced the risk of oral/mouth and pharyngeal cancers. (Carlotta Galeone et al, Int J Cancer., 2015)
The study also highlighted that the highest risk of oral and pharyngeal cancer was observed in heavy alcohol drinkers with low folate intake as compared to never/light drinkers with high folate intake.
Findings from these studies suggest that including folate rich foods such as broccoli, brussels sprouts, leafy green vegetables such as kale, spring greens and spinach, to the diet might help reduce the risk of oral cavity/mouth and oropharyngeal cancers.
Diet/Foods or Oral Habits that may Increase the Risk of Oral and Oropharyngeal Cancer
Chewing Tobacco and Areca Nut may Increase the Risk of Oral Cancer
A meta-analysis of 15 studies done by the researchers of Griffith University in Australia evaluated the association between the use of oral smokeless tobacco in any form, areca nut, and betel quid (which contains betel leaf, areca nut/betel nut and slaked lime) without tobacco and the incidence of oral/mouth cancer in South Asia and the Pacific. The studies for the analysis were obtained through literature search in Pubmed, CINAHL and Cochrane databases till June 2013. (Bhawna Gupta and Newell W Johnson, PLoS One., 2014)
The analysis found that chewing tobacco is significantly associated with an increased risk of oral cavity/mouth cancer. The study also found that the use of betel quid (containing betel leaf, areca nut / betel nut and slaked lime) without tobacco also resulted in an increased risk of oral/mouth cancer, possibly due to the carcinogenicity of areca nut.
Avoid chewing tobacco and areca nut to stay away from the risk of developing oral/mouth and oropharyngeal cancer and also gain maximum benefit from the treatment.
Alcohol Consumption may increase the Risk of Oral and Oropharyngeal Cancer
A systematic review done by the Mario Negri Institute for Pharmacological Research in Milan, Italy evaluated whether alcohol consumption causes mouth cancer and other cancers. The study found that compared to people who never drank or drank only occasionally, consuming more than 4 drinks of alcohol per day was associated with a 5 fold increased risk of oral/mouth, pharyngeal cancer and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, 2.5 fold increased risk of laryngeal cancer, 50% increased risk of colorectal and breast cancers, and 30% increased risk of pancreatic cancer. The review also mentioned that even low doses of alcohol consumption of ≤1 drink/day increased the risk of oral/mouth and pharyngeal cancer by about 20% and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by 30%. (Claudio Pelucchi et al, Nutr Cancer., 2011)
Another study done by the Kaohsiung Medical University in Taiwan also found that Tobacco-free betel-quid, along with alcohol and/or tobacco consumption, resulted in a much earlier occurrence of oral cavity cancer. Alcohol and tobacco intake bestowed increased risks of earlier tumor occurrence. (Chien-Hung Lee et al, J Oral Pathol Med., 2011)
Avoid drinking alcohol to stay away from the risk of developing oral/mouth and oropharyngeal cancer and also gain maximum benefit from the treatments.
Note : Alcohol consumption and tobacco use may also interfere with the mouth or oropharyngeal cancer treatments and may also aggravate the symptoms.
Yerba Mate Consumption and the Risk of Mouth and Oropharyngeal Cancer
Few Studies had previously suggested that drinking hot yerba mate might increase the risk of oral and pharyngeal cancers. However, it is unclear whether the increased risk is due to the high temperature of the beverage when it was consumed or due to some carcinogenic components present in maté. (Ananda P Dasanayake et al, Oral Oncol., 2010)
The association between mate consumption and oral cavity or oropharyngeal cancer is hence inconclusive.
Other Foods Associated with Oropharyngeal Cancer
When it comes to oropharyngeal cancer care and prevention, some vegetables and foods such as cauliflower, cocoa, peppermint, mustard and currant may not help. Also, it is better to avoid using dietary supplements of cabbage, nutmeg, poppy, clove and fava bean when facing mouth and oropharyngeal cancer and working towards reducing the symptoms.
Conclusion
Diet plays an important role in reducing or increasing the risk of developing different types of cancers including oral and oropharyngeal cancer. It is very important to take the right foods to prevent the risk of developing oral cavity/mouth or oropharyngeal cancer and also to support the treatment and reduce the aggressiveness of the symptoms of this life threatening disease. When it comes to oral cancer, eating certain cruciferous vegetables and other vegetables and fruits (such as banana and avocado), taking turmeric, button mushrooms, drinking coffee, following a Mediterranean diet (with sorghum), and taking folate rich foods might help reduce the risk of developing the cancer. Following a proper, healthy diet/nutrition is a fundamental part of any cancer therapy including the therapy for oral/mouth and oropharyngeal cancer, without which other treatment modalities that are used to alleviate the symptoms, are less likely to succeed.
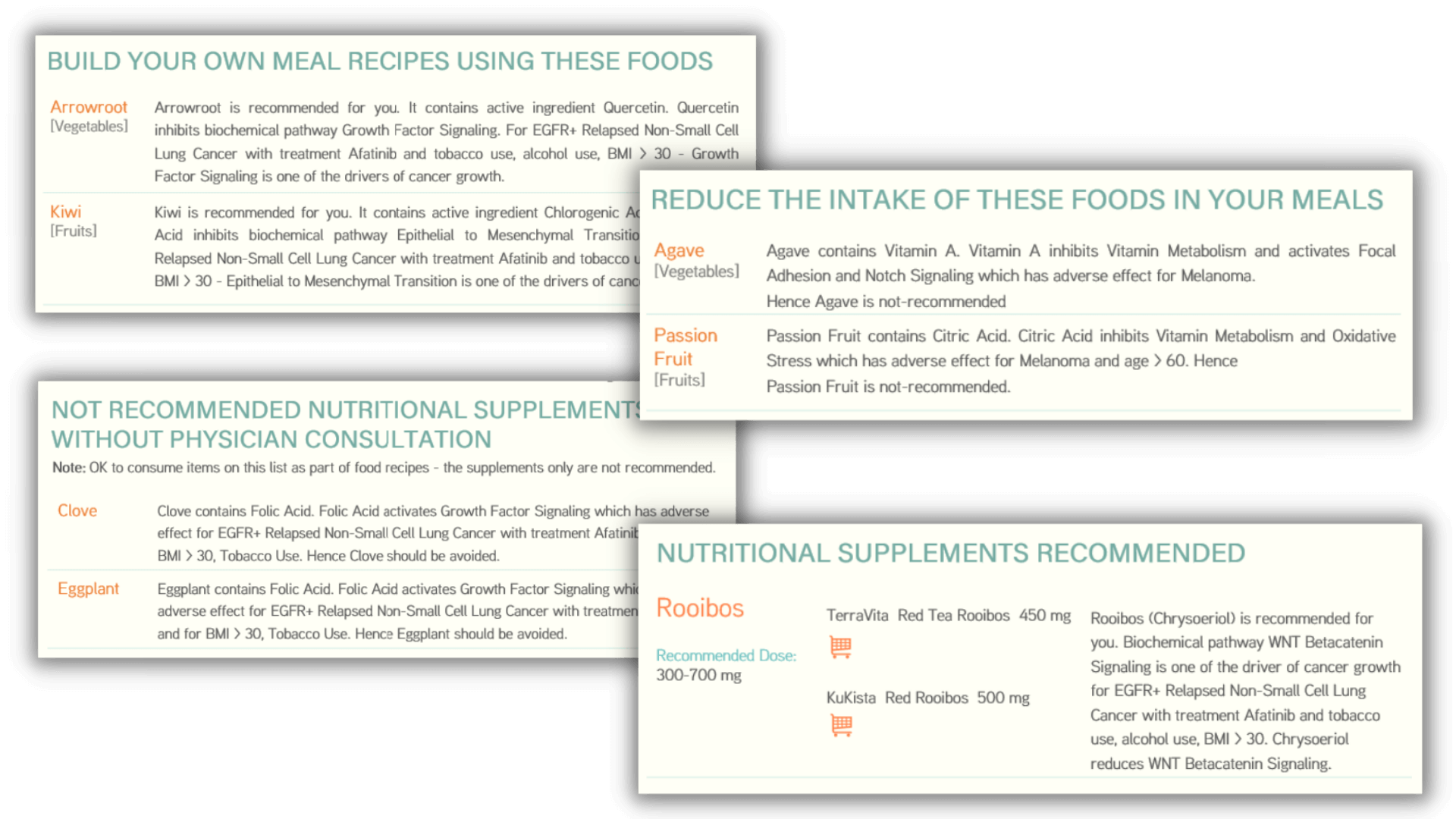
What food you eat and which supplements you take is a decision you make. Your decision should include consideration of the cancer gene mutations, which cancer, ongoing treatments and supplements, any allergies, lifestyle information, weight, height and habits.
The nutrition planning for cancer from addon is not based on internet searches. It automates the decision making for you based on molecular science implemented by our scientists and software engineers. Irrespective of whether you care to understand the underlying biochemical molecular pathways or not - for nutrition planning for cancer that understanding is needed.
Get started NOW with your nutrition planning by answering questions on the name of cancer, genetic mutations, ongoing treatments and supplements, any allergies, habits, lifestyle, age group and gender.
Personalized Nutrition for Cancer!
Cancer changes with time. Customize and modify your nutrition based on cancer indication, treatments, lifestyle, food preferences, allergies and other factors.
Cancer patients often have to deal with different chemotherapy side effects which affect their quality of life and look out for alternative therapies for cancer. Taking the right nutrition and supplements based on scientific considerations (avoiding guesswork and random selection) is the best natural remedy for cancer and treatment related side-effects.
